CHECK RUBBER BELLOWS, BOOTS AND CLAMPING RINGS
Careless driving and dirt accumulation significantly increase the risk of wear on safety-relevant chassis and steering components. Technicians need to pay attention to typical damage patterns and remedy defects as required. If chassis or steering components are damaged, the person steering needs to expect the handling of their vehicle to become critical. Experts at ZF Aftermarket therefore advise workshops to inform their customers of how important a regular inspection is. Many components can be affected.

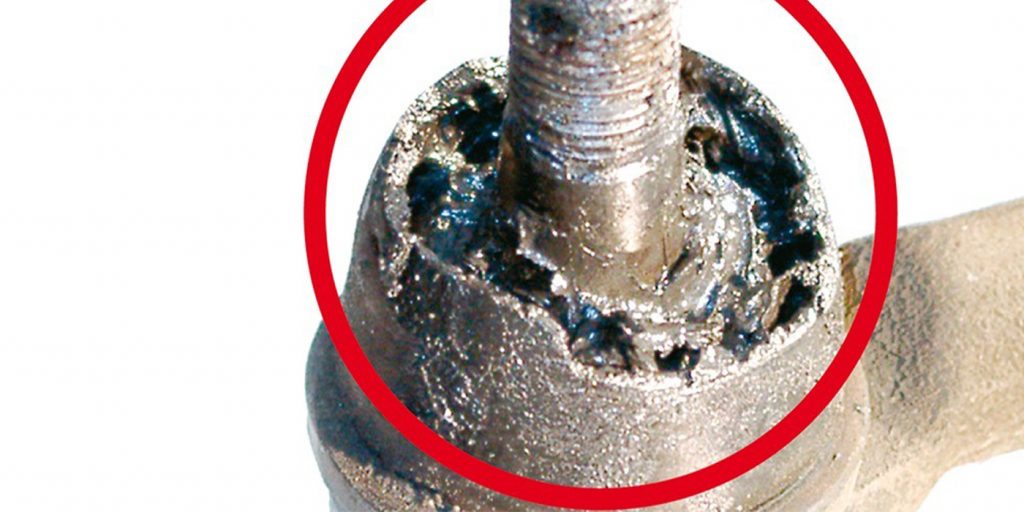
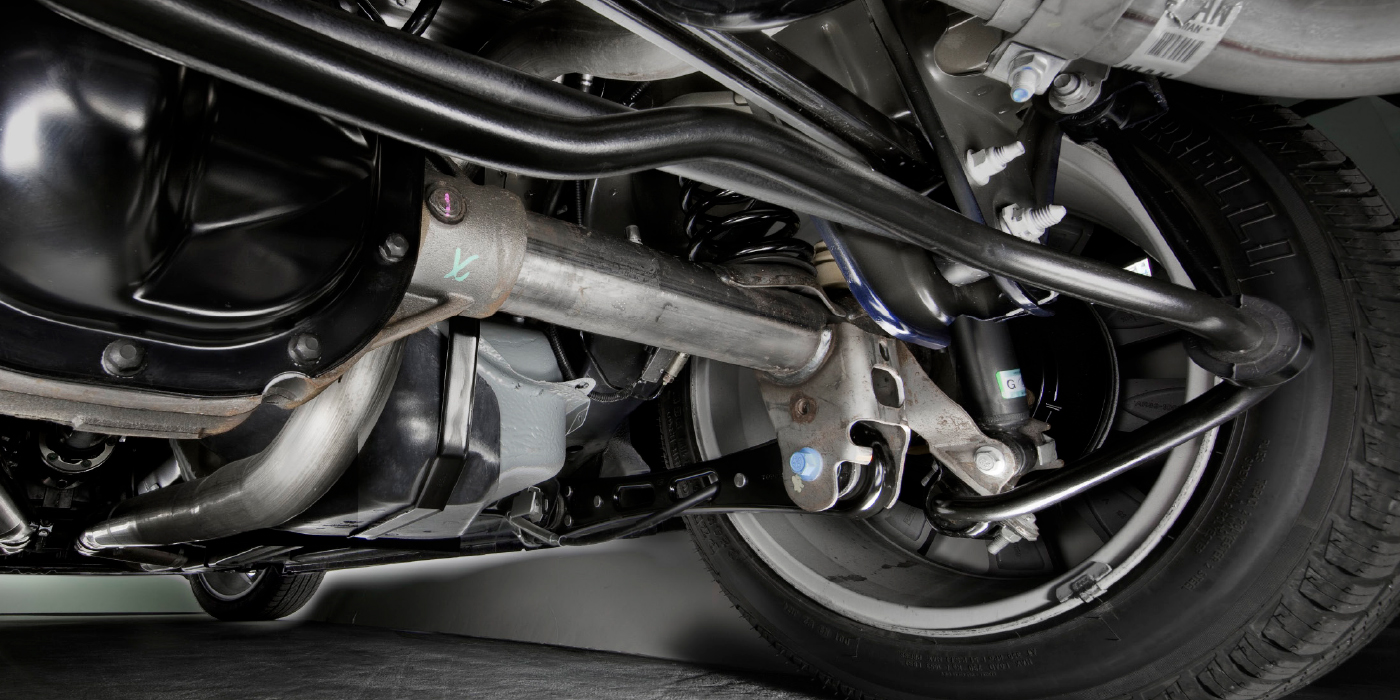
Technicians should particularly check whether the rubber bellows on the joints are worn, damaged or leaking. Because any splash water that gets in washes out the special grease, this then allows dirt particles to enter the joint. These particles destroy the inner plastic spherical shell and damage both the ball stud and the joint housing. This means that the clearance in the joint no longer meets the standard. Within the steering, the tie rod requires special attention: Apart from the rubber bellows, the steering boot needs to be checked for damage. The spring clamping rings should also be looked at so that any spots of rust are already identified as soon as they appear.

CURB CONTACT WITH CONSEQUENCES
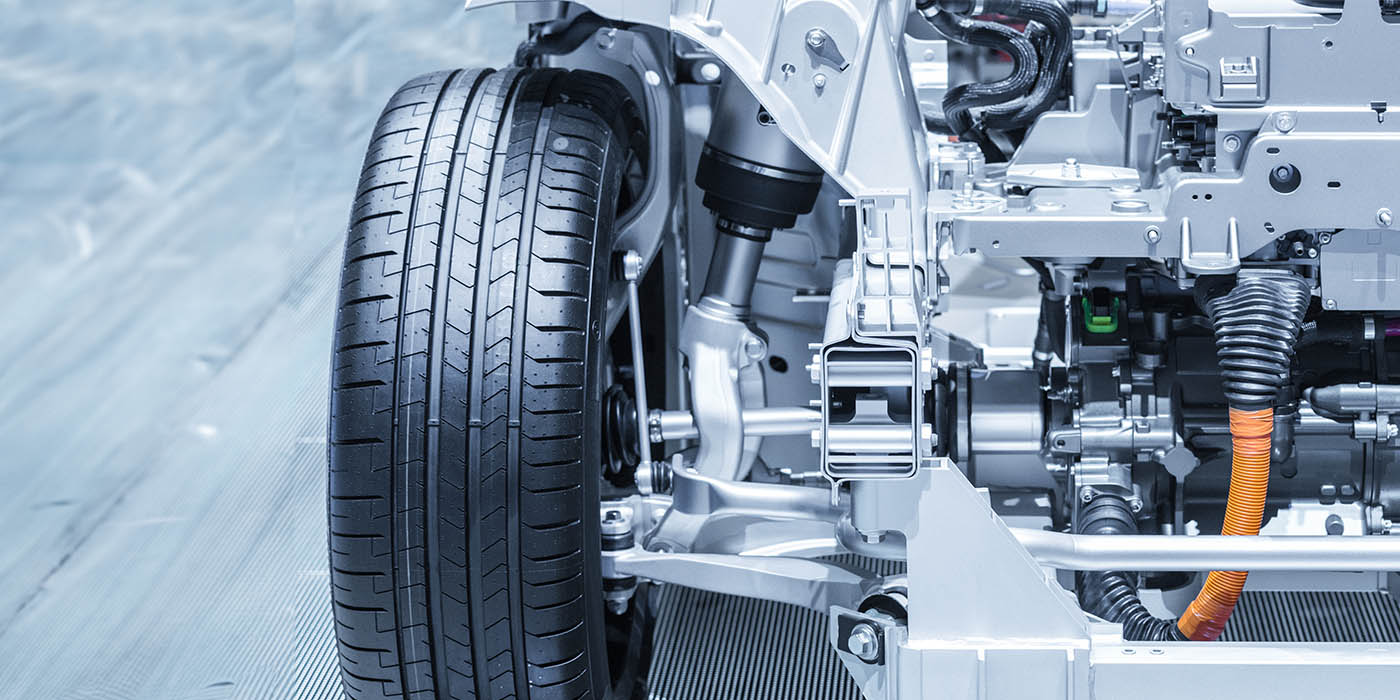
On the chassis, the supporting joint, control arms and the stabilizer can show serious damage caused by corrosion, invaded foreign objects or dirt accumulation. In addition, driving over curbs is often the cause of defects. The consequences of damage greatly impair the vehicle handling and thus, the driver’s safety. Apart from that, they often lead to increased wear on other chassis components as well as to tires wearing unevenly and worse riding comfort. This means higher risk of accidents and additional repair expenses.
REGULAR VEHICLE INSPECTION

ZF Aftermarket recommends special tools for professional and smooth inspection or removal of supporting joints. This minimizes the risk of injury and reduces repair costs. ZF Aftermarket feels obliged to draw attention to the need for regular vehicle inspections: After all, the idea is to improve safety on the roads.
Courtesy of ZF